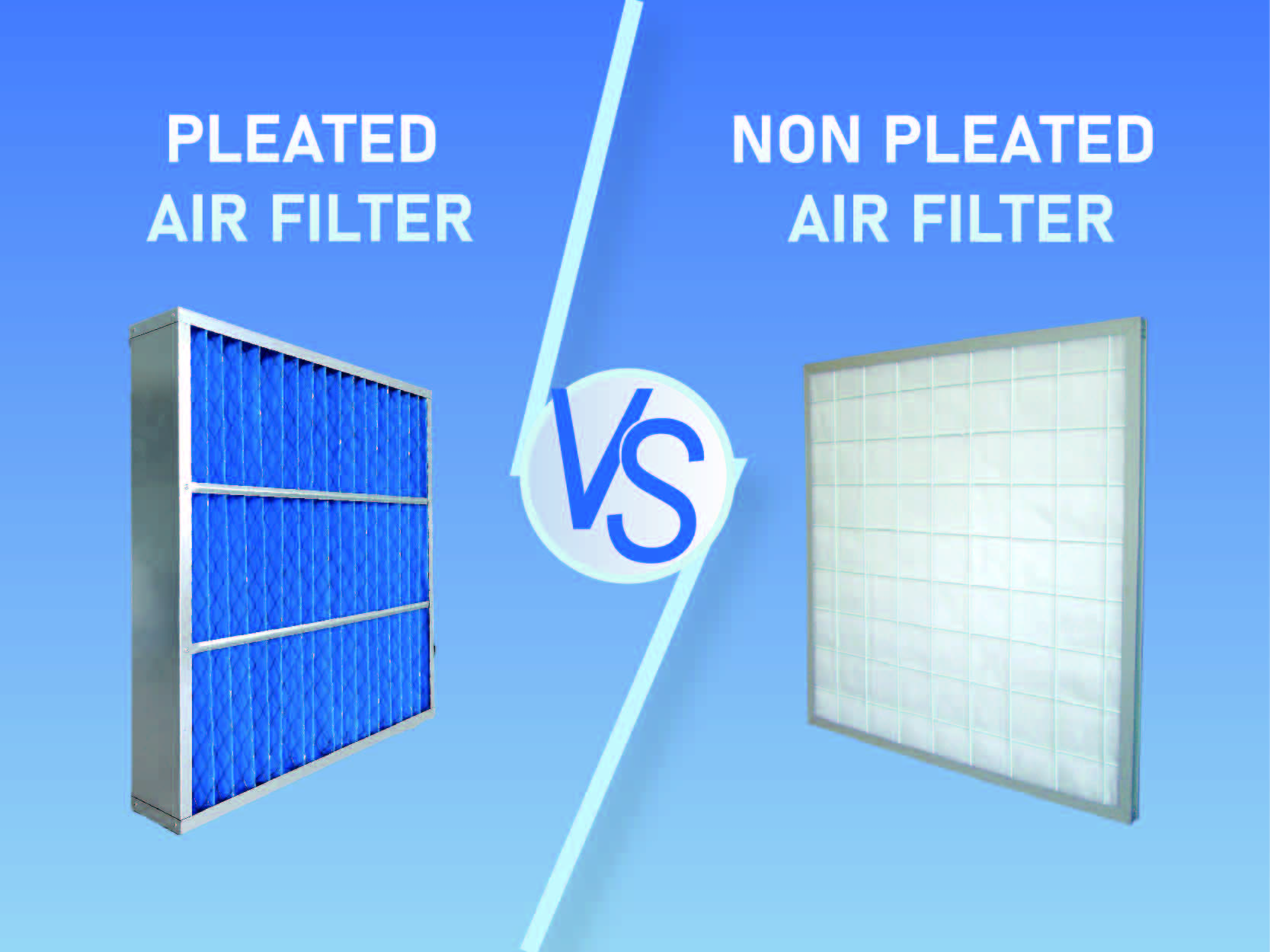
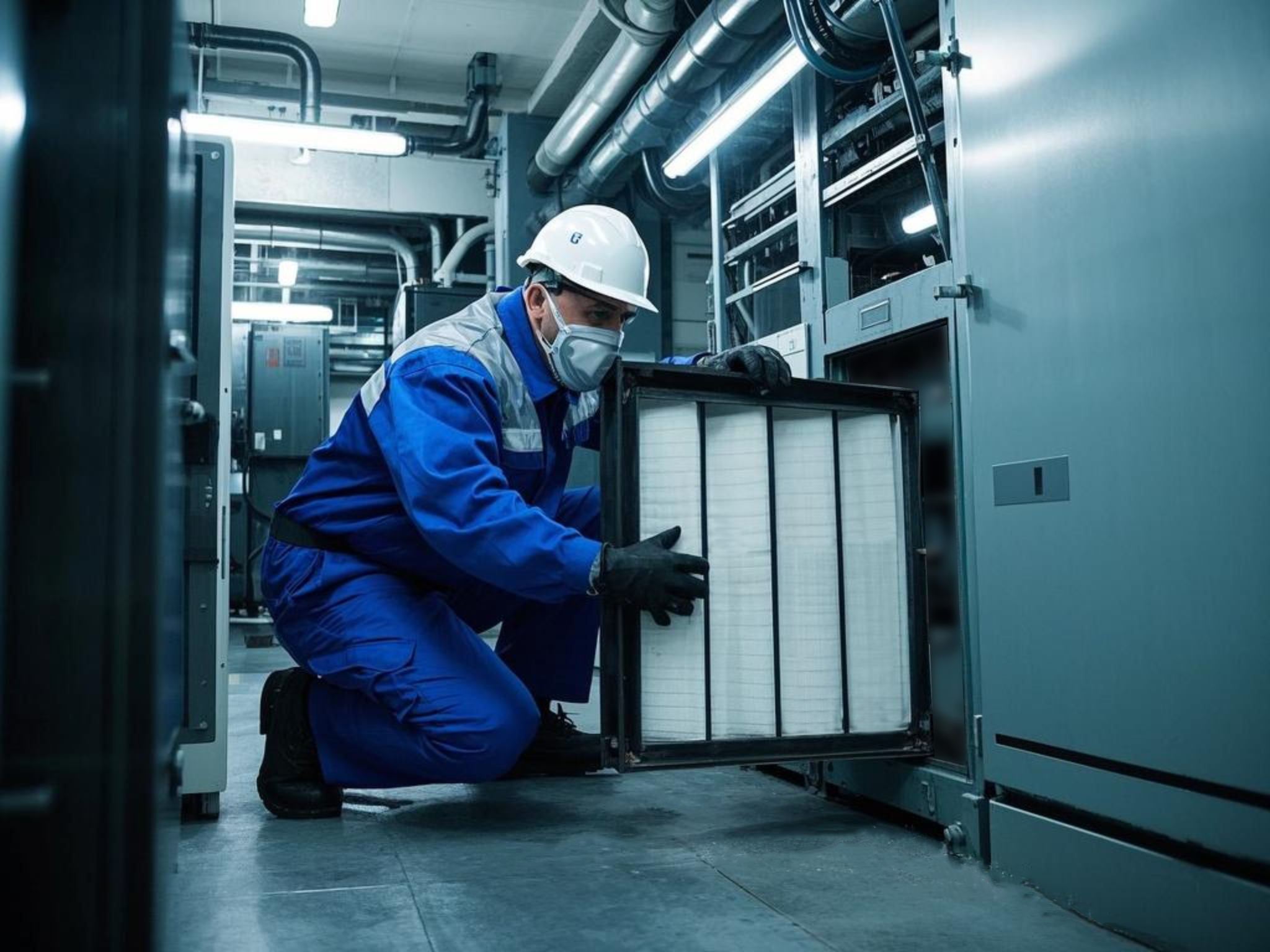
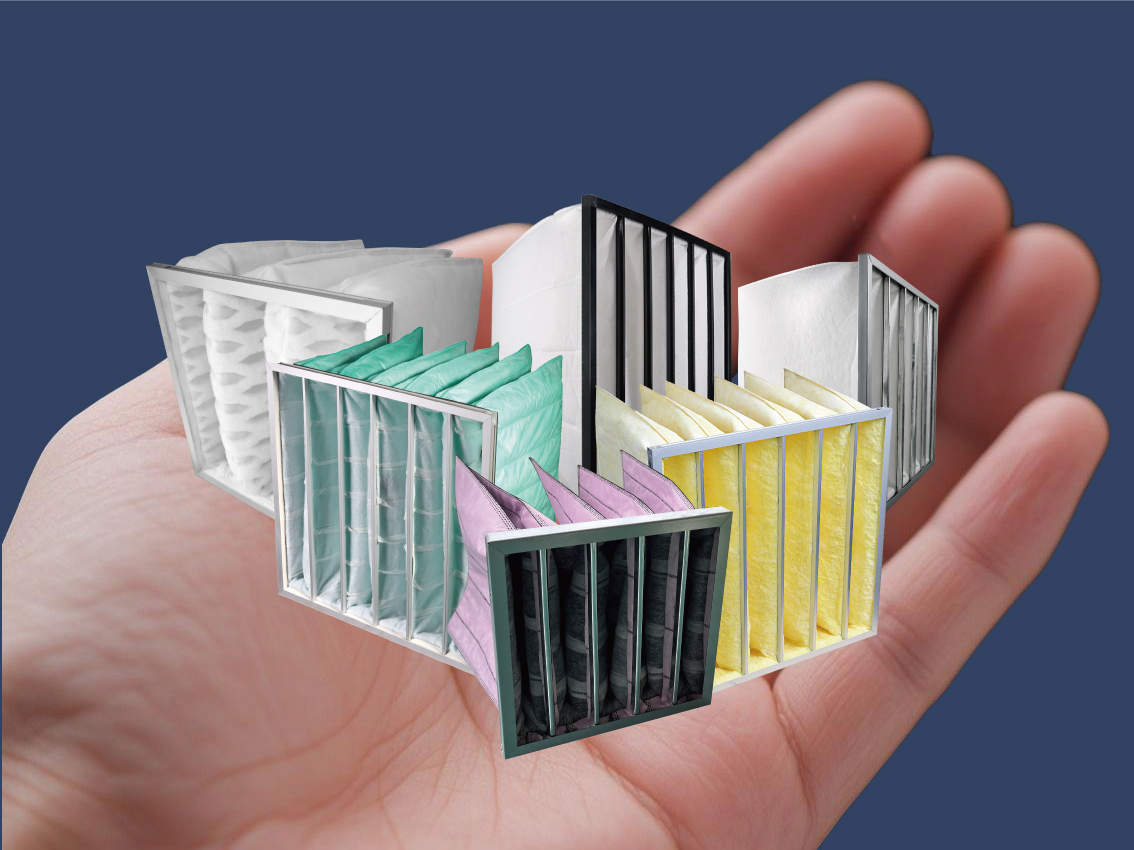
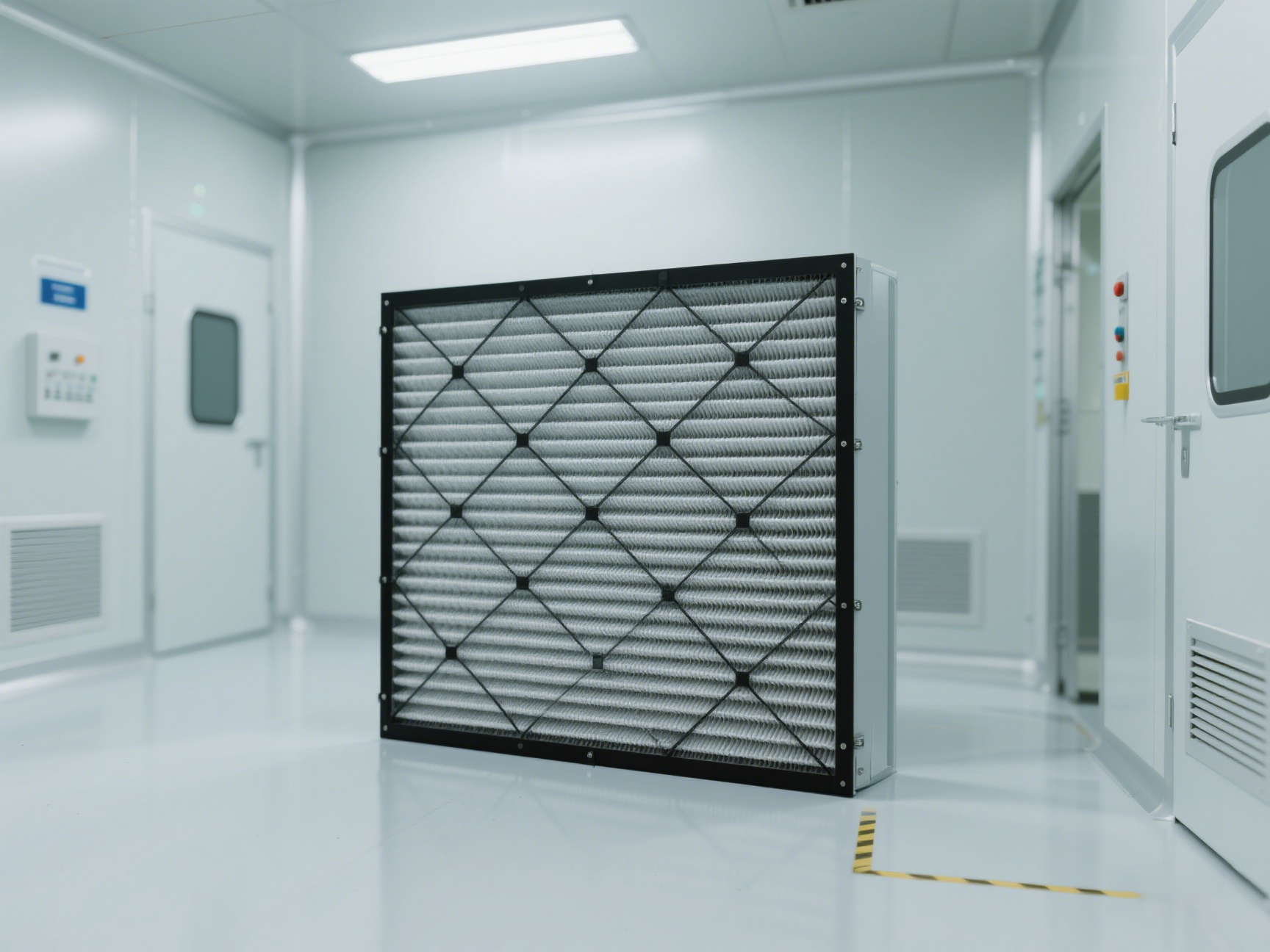
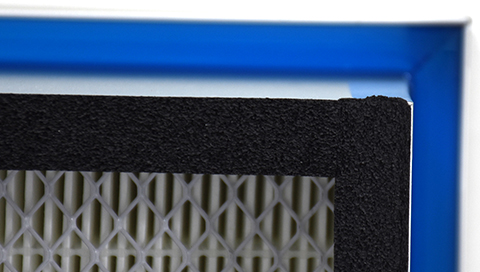
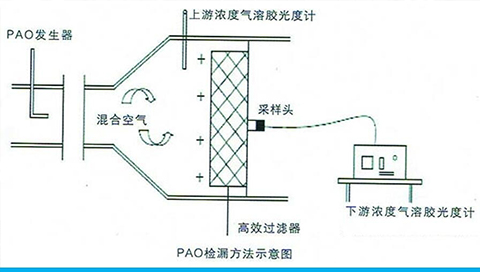
Pocket filters consist of multiple fabric pockets, typically made from polyester or fiberglass, arranged in a frame to optimize airflow and filtration efficiency. These filters trap airborne particles through mechanical interception, diffusion, and inertial impaction. Their high dust-loading capability and low-pressure drop make them ideal for applications requiring consistent air purity with minimal energy consumption.
In electronics manufacturing, pocket filters play a critical role in maintaining contaminant-free environments. They prevent dust, static particles, and chemical vapors from damaging sensitive components during production. By ensuring clean air circulation, these filters reduce defects, improve yield rates, and comply with industry standards like ISO 14644 for cleanroom classifications. Their durability and efficiency directly impact product quality and operational costs.
Unlike flat-panel or cartridge filters, pocket filters offer a larger surface area due to their extended pocket design. This allows them to trap more particulate matter with lower resistance, resulting in better energy efficiency and longer service life compared to traditional filtration methods.
Filter efficiency is measured by standards such as MERV and HEPA. Pocket filters typically range from MERV 8 to MERV 15, balancing fine particle capture with airflow requirements, making them suitable for applications demanding moderate to high filtration performance.
Electrostatic filters use an electric charge to attract and capture airborne particles, including dust, pollen, and microbes. Unlike mechanical filters, they rely on static electricity to enhance particle adhesion, improving efficiency without significantly increasing airflow resistance.
In environments requiring ultra-clean air (hospitals, labs, or electronics manufacturing), electrostatic filters complement mechanical filtration by capturing sub-micron particles. They are particularly effective against smoke, bacteria, and viruses, making them a key component in advanced air purification systems.
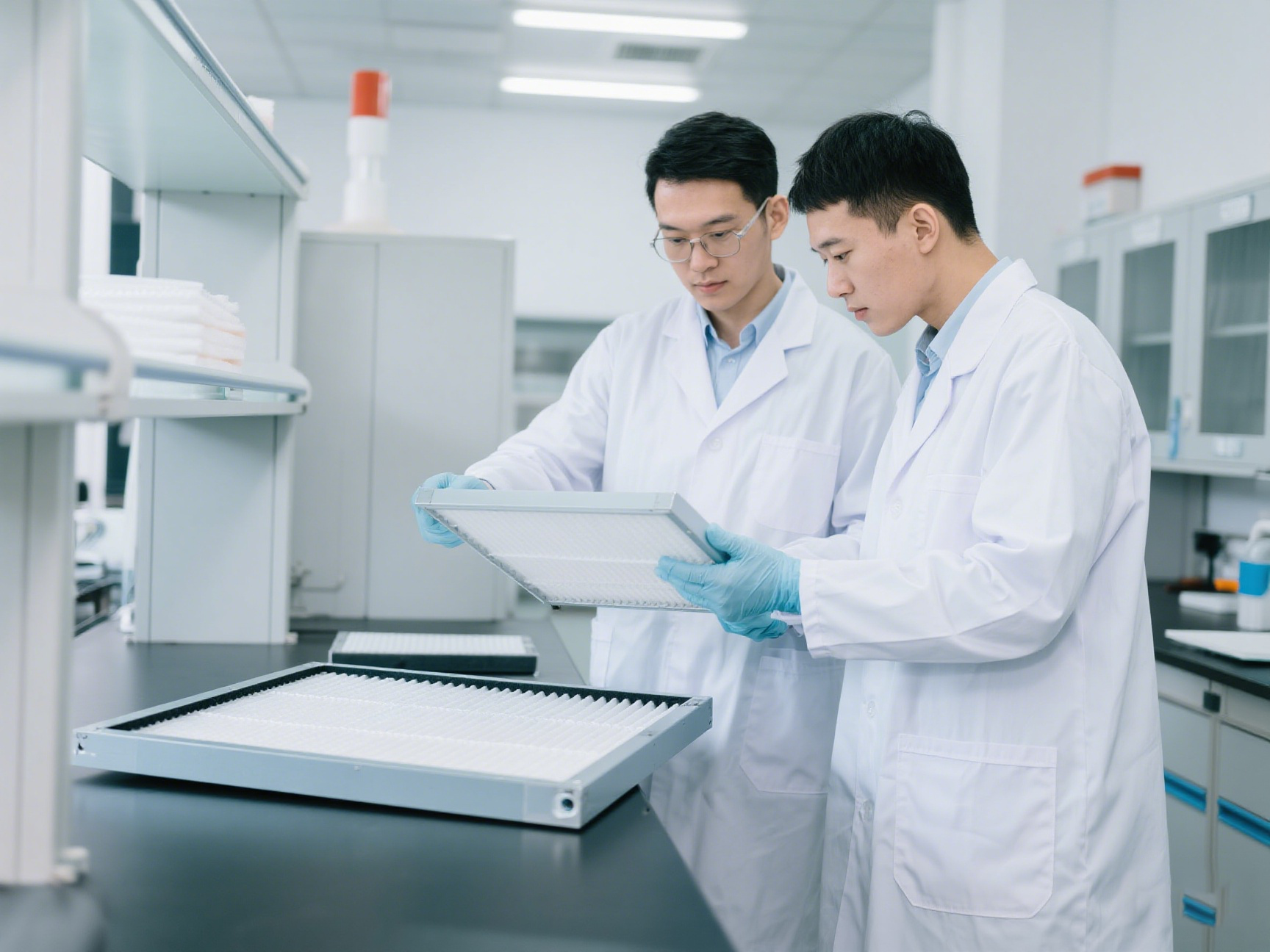

Electronics factories generate various types of dust, including:
Silica & Ceramic Particles: From PCB drilling and component handling.
Metal Shavings: Produced during machining and assembly.
Plastic & Fiber Debris: From packaging and insulation materials.
Static-Attracted Microdust: Fine particles that cling to sensitive electronic components.
Pocket filters excel in dust control due to their deep-pleated design, which increases surface area for particle capture. Their high dust-holding capacity and low airflow resistance make them ideal for continuous operation in electronics factories, reducing maintenance frequency while ensuring consistent air quality.
Semiconductor Facility: Implementation of MERV 13 pocket filters reduced airborne particles by 85%, improving chip yield rates.
PCB Manufacturing Plant: Combined pocket and electrostatic filters cut dust-related defects by 60%, extending equipment lifespan.
Cleanroom Assembly Line: Upgrading to HEPA-grade pocket filters achieved ISO Class 5 compliance, critical for microelectronics production.
Cleanrooms are classified under ISO 14644-1 standards based on allowable particle counts per cubic meter. For example:
ISO Class 5 (≤3,520 particles ≥0.5µm/m³) – Common in semiconductor fabrication
ISO Class 7 (≤352,000 particles ≥0.5µm/m³) – Typical for medical device manufacturing
Pocket filters help maintain these classifications by effectively removing airborne contaminants that could compromise sensitive processes.
In cleanroom air handling systems, pocket filters are typically installed:
As pre-filters to extend HEPA/ULPA filter lifespan
In recirculation air systems for particle control
At critical process points for localized filtration
Their pleated design provides optimal balance between high dust-holding capacity and minimal airflow restriction, essential for maintaining cleanroom pressure differentials.
The use of pocket filters in cleanroom environments directly enhances product quality by:
Reducing particulate contamination on sensitive components
Minimizing defects in precision manufacturing processes
Extending the service life of expensive HEPA/ULPA filters
Maintaining consistent environmental conditions for process stability
This results in higher yields, reduced scrap rates, and improved reliability of final products in critical industries.
While pocket filters may carry a slightly higher initial cost compared to basic panel filters, their superior durability and efficiency translate to:
30-50% longer service intervals than conventional filters
Reduced energy consumption due to lower pressure drop
Fewer system shutdowns for filter changes
This creates a compelling ROI, often paying back the initial premium within the first year of operation through reduced replacement and energy costs.
Pocket filters are designed for easy maintenance with features like:
Visual pressure drop indicators for timely replacement
Washable/reusable options for certain models
Quick-release frames for minimal downtime during changes
Proper maintenance scheduling can extend filter life by 20-30%, while strategic stocking of replacements prevents costly production interruptions.
The implementation of pocket filters affects operational budgets through:
Energy Savings: Their low resistance design can cut HVAC energy use by 15-25%
Labor Efficiency: Reduced change frequency decreases maintenance man-hours
Waste Reduction: Longer life means fewer spent filters for disposal
Production Uptime: Consistent air quality minimizes contamination-related stoppages
Facilities typically see a 40-60% reduction in total filtration costs over a 5-year period when switching to high-quality pocket filters.
Pocket filters represent a smart, efficient solution for industries requiring reliable air filtration, from electronics manufacturing to pharmaceuticals and cleanroom environments. Their enhanced dust-holding capacity, energy efficiency, and long service life make them a cost-effective upgrade over traditional filters.